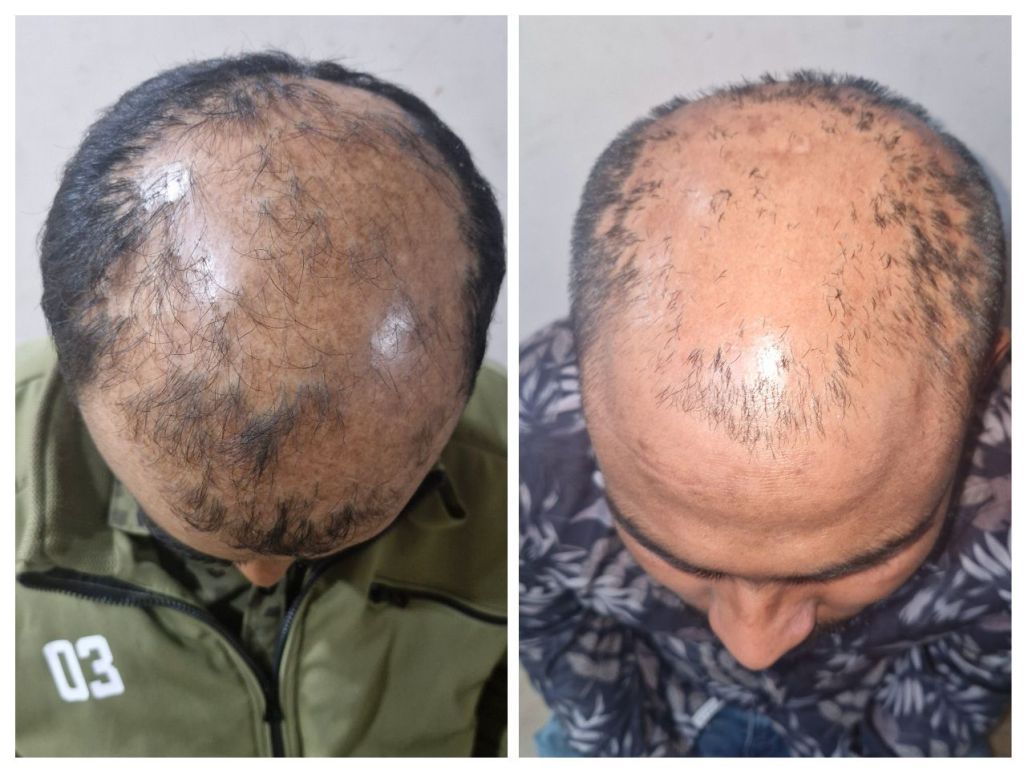
Alopecia areata is an autoimmune condition where the immune system attacks hair follicles, leading to hair loss. While steroid injections and other medical treatments are effective for many patients, some individuals may not respond to these therapies due to several factors:
1. Severity and Extent of Disease
- Chronic or Extensive Involvement: Patients with more widespread hair loss (alopecia totalis or universalis) are less likely to respond to treatment compared to those with small, localized patches.
- Long-standing Disease: Hair follicles that have been inactive for a prolonged period may become less responsive to stimulation.
2. Immune System Dysregulation
- Resistance to Immunosuppression: Some patients’ immune systems may not be sufficiently suppressed by steroids, allowing the autoimmune attack on hair follicles to continue.
- Cytokine Imbalance: Persistent inflammation driven by cytokines (e.g., IFN-γ, IL-15) may not be fully counteracted by corticosteroids.
3. Genetic Factors
- Genetic Predisposition: Certain genetic profiles linked to alopecia areata can influence treatment responsiveness. For example, specific HLA gene variants are associated with more severe or treatment-resistant forms.
4. Delayed Treatment Initiation
- Timing Matters: Early intervention often leads to better outcomes. Delay in starting treatment can allow more extensive follicular damage, reducing the likelihood of regrowth.
5. Treatment Limitations
- Insufficient Dosage or Duration: Inadequate steroid dosage, frequency, or duration may not effectively suppress inflammation.
- Tachyphylaxis: Prolonged steroid use can lead to diminishing returns as the body adapts, reducing efficacy over time.
6. Comorbid Conditions
- Other Autoimmune Diseases: Coexisting autoimmune conditions (e.g., thyroid disease, vitiligo) may exacerbate immune dysregulation, complicating treatment response.
- Nutritional Deficiencies: Deficiencies in vitamins (e.g., vitamin D, zinc) can hinder hair regrowth.
7. Psychological and Stress Factors
- Chronic Stress: Psychological stress can worsen immune dysregulation, reducing the effectiveness of treatments.
- Emotional Trauma: Stress-related hormonal changes may amplify hair follicle dysfunction.
Alternative Approaches for Resistant Cases:
- JAK Inhibitors: Emerging therapies like tofacitinib and baricitinib target the JAK-STAT pathway and have shown promise in refractory cases.
- Immunotherapy: Contact immunotherapy (e.g., diphenylcyclopropenone) may stimulate hair regrowth by modulating the immune response.
- Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP): May enhance follicle recovery in steroid-resistant cases.
Would you like more details on advanced treatment options or specific therapies?
कुछ मरीजों में एलोपेसिया एरीटा (Alopecia Areata) स्टेरॉयड इंजेक्शन और अन्य चिकित्सीय उपचारों का जवाब क्यों नहीं देता, इसके पीछे कई कारण हो सकते हैं:
1. रोग की तीव्रता और विस्तार
- व्यापक या पुरानी अवस्था: जिन मरीजों में बालों का झड़ना व्यापक (एलोपेसिया टोटालिस या यूनिवर्सालिस) होता है, उनमें उपचार का असर कम होता है।
- लंबे समय से मौजूद बीमारी: जिन बालों के कूप (hair follicles) लंबे समय से निष्क्रिय हैं, वे उपचार के प्रति कम संवेदनशील हो सकते हैं।
2. प्रतिरक्षा प्रणाली (इम्यून सिस्टम) की असंतुलित प्रतिक्रिया
- इम्यूनोसप्रेशन का प्रतिरोध: कुछ मरीजों की प्रतिरक्षा प्रणाली स्टेरॉयड से पर्याप्त रूप से दबती नहीं है, जिससे बालों के कूप पर हमला जारी रहता है।
- साइटोकाइन असंतुलन: कुछ रोगियों में इन्फ्लेमेटरी साइटोकाइन्स (जैसे IFN-γ, IL-15) स्टेरॉयड के प्रभाव को निष्क्रिय कर सकते हैं।
3. आनुवंशिक कारण
- आनुवंशिक प्रवृत्ति: कुछ जीन विशेष रूप से HLA जीन में बदलाव, एलोपेसिया एरीटा के गंभीर और उपचार-प्रतिरोधी रूपों से जुड़े होते हैं।
4. उपचार शुरू करने में देरी
- समय पर उपचार का अभाव: यदि उपचार देर से शुरू किया जाए तो बालों के कूप को अधिक नुकसान हो सकता है, जिससे पुनः उगने की संभावना कम हो जाती है।
5. उपचार की सीमाएँ
- खुराक या अवधि की अपर्याप्तता: यदि स्टेरॉयड की खुराक या अवधि पर्याप्त नहीं है, तो सूजन को दबाया नहीं जा सकता।
- टैकीफाइलैक्सिस: लंबे समय तक स्टेरॉयड के उपयोग से शरीर इसके प्रति प्रतिरोधकता विकसित कर सकता है, जिससे प्रभाव कम हो जाता है।
6. सहवर्ती बीमारियाँ (Comorbid Conditions)
- अन्य ऑटोइम्यून रोग: थायरॉइड विकार या विटिलिगो जैसी अन्य ऑटोइम्यून बीमारियाँ उपचार को जटिल बना सकती हैं।
- पोषण की कमी: विटामिन डी, जिंक जैसी पोषक तत्वों की कमी बालों की पुनः वृद्धि में बाधा बन सकती है।
7. मनोवैज्ञानिक और तनाव से जुड़े कारक
- क्रोनिक स्ट्रेस: लंबे समय तक तनाव इम्यून सिस्टम को असंतुलित कर सकता है, जिससे उपचार की प्रभावशीलता कम हो जाती है।
- भावनात्मक आघात: मानसिक आघात से हार्मोनल परिवर्तन हो सकते हैं, जिससे बालों के कूप कमजोर हो जाते हैं।
स्टेरॉयड-प्रतिरोधी मामलों के लिए वैकल्पिक उपचार:
- JAK इनहिबिटर्स: टॉफासिटिनिब और बैरिसिटिनिब जैसे नए उपचार प्रतिरक्षा मार्ग (JAK-STAT पाथवे) को लक्षित करते हैं और जटिल मामलों में कारगर साबित हुए हैं।
- संपर्क इम्यूनोथेरेपी: डिफेनाइलसाइक्लोप्रोपेनोन (DPCP) जैसे टॉपिकल एजेंट प्रतिरक्षा प्रतिक्रिया को संशोधित कर सकते हैं।
- प्लेटलेट-रिच प्लाज़्मा (PRP): स्टेरॉयड-प्रतिरोधी मामलों में बालों के कूप की पुनः सक्रियता में मदद कर सकता है।
यदि आप उन्नत उपचार विकल्पों या विशिष्ट थैरेपी के बारे में अधिक जानकारी चाहते हैं, तो बताइए।
Leave a comment